Types of Memory Management Techniques to Manage Server Performance
- March 19, 2018
- 0
Memory management is a crucial thing in order to manage server performance. The servers are always expected to function 24/7 without any hints of delay or underperformance. Hence, accumulating data in an organized manner is a symbol of better conduct. A third party client always anticipates for whatever it has requested and wouldn’t wait for longer than a few seconds. The server, therefore, has to manage somehow that how it would allocate the free space, from where it would bring that free space, and so on. Types of memory management assure that there are various kinds of memory management techniques and any one or combination of two or more could be acquired in order to manage server performance in general.
Types of Memory Management
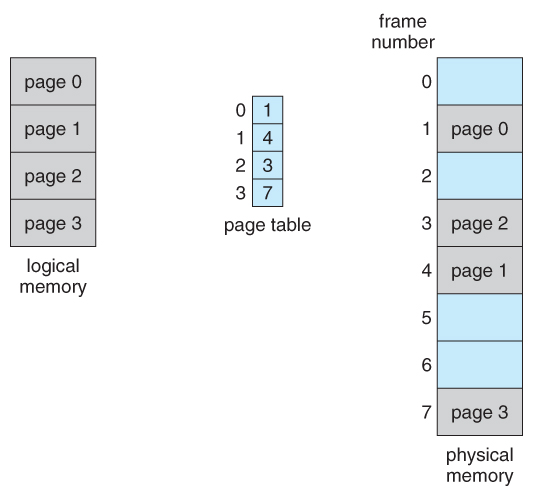
Memory paging: Paging is one of the types of memory management techniques done by the computer operating system. In this method, if the main memory (RAM) isn’t available at the moment, the secondary storage (disk or hard disk) would be used as the main memory. The operating system retrieves the data in blocks of the same size that are called pages. It does have a downside, which is – the time taken to retrieve the data from disk would be slower as compared to that of RAM. So, it would be just a temporary fix.
 Memory mirroring: It is one of the best memory management techniques in which the physical memory is separated into two logical channels, and the first channel mirrors the second one. So, if the main memory is temporarily not in use, its mirror would be set to function till it gets back to normal working. Everything is done by the memory controller without downtime and without client’s notice.
Memory mirroring: It is one of the best memory management techniques in which the physical memory is separated into two logical channels, and the first channel mirrors the second one. So, if the main memory is temporarily not in use, its mirror would be set to function till it gets back to normal working. Everything is done by the memory controller without downtime and without client’s notice.
Memory overcommit: It is a concept in which more memory is assigned to VM than it is physically available on the host. It is not disadvantageous most of the times since the virtual machines not necessarily need to use the whole allocated memory.
For instance, let us suppose there are 4 VM each of which has 1 GB of memory on a physical machine. The physical machine provides 4 GB of memory but those VM do not use more than 500 MB. So, if we assume that 2 GB of memory is still left untouched, we can add more virtual machines. The trouble arises if all of them start using the memory more than required, or any one or more are using significantly higher margin.
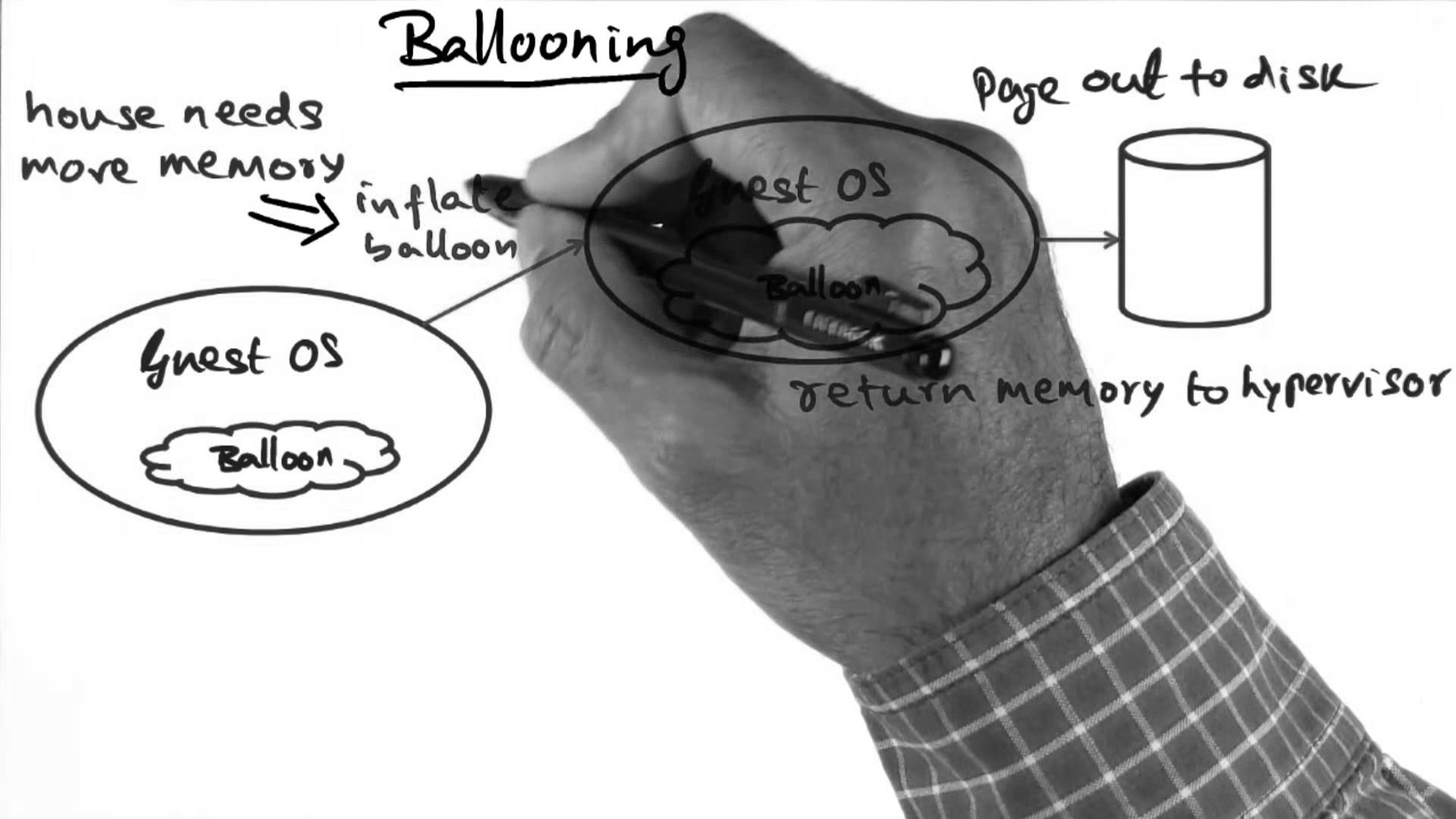
Memory ballooning: It is a process in memory paging in which the spare memory space is made available to the host if it is not in use at all, and that will be allocated to those systems where there is an urgent requirement of the memory. There are balloon drivers in each VM in order to identify the unused memory to make it available to the host for further usage.
For instance, if 10 GB of memory had been allocated for 1 virtual machine but only 5 GB is in use then the rest 50% of the memory could be determined by the balloon drivers and distributed to other virtual machines on the same host that are running low in memory.
 Transparent page sharing: It is a common scenario in which multiple virtual machines run the same OS, identical memory pages exist that result in redundancies. The hypervisor discovers it by assigning hash values to the pages and by comparing them bit-by-bit. The comparison is done when those hash values seem to match.
Transparent page sharing: It is a common scenario in which multiple virtual machines run the same OS, identical memory pages exist that result in redundancies. The hypervisor discovers it by assigning hash values to the pages and by comparing them bit-by-bit. The comparison is done when those hash values seem to match.
If the hypervisor finally detects the identical memory pages on multiple VMs on a host, instead of keeping additional memory space for similar pages, it shares them among VMs with pointers. If the existing data changes, the hypervisor writes the memory to new page and then readdresses a pointer. In general, small memory pages are identical. The concept is, therefore, not applicable for large memory pages.
Sometimes the servers do not function properly, despite doing the right kind of settings in the department of memory management. Yet a person may face server down issues at times that never seem to resolve. Apachebooster deals with slow working servers. It is a cPanel plugin that contains the combination of Nginx and Varnish.




